Cancer services
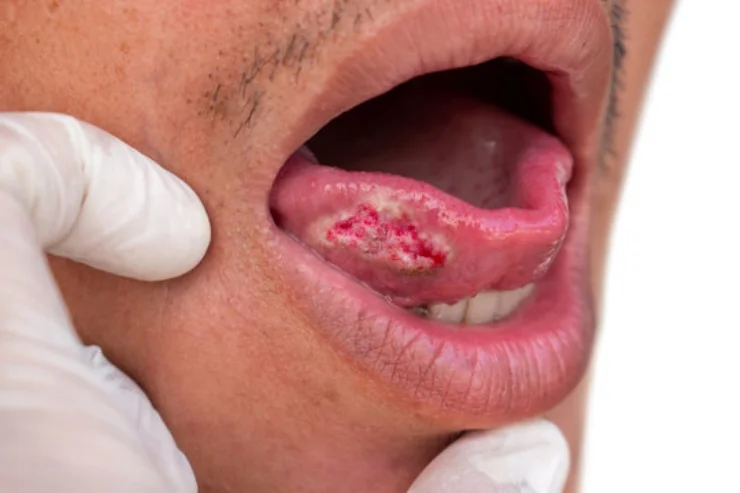
Oral Cancer
Oral cancer affects the mouth, lips, tongue, and throat, often linked to tobacco, alcohol, and HPV infection. Symptoms include persistent sores, pain, difficulty swallowing, and white or red patches. Early diagnosis improves survival, with treatments including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Regular dental checkups and avoiding risk factors significantly reduce chances. Awareness and early intervention play crucial roles in improving outcomes, making education and routine screenings essential for oral cancer prevention and management.
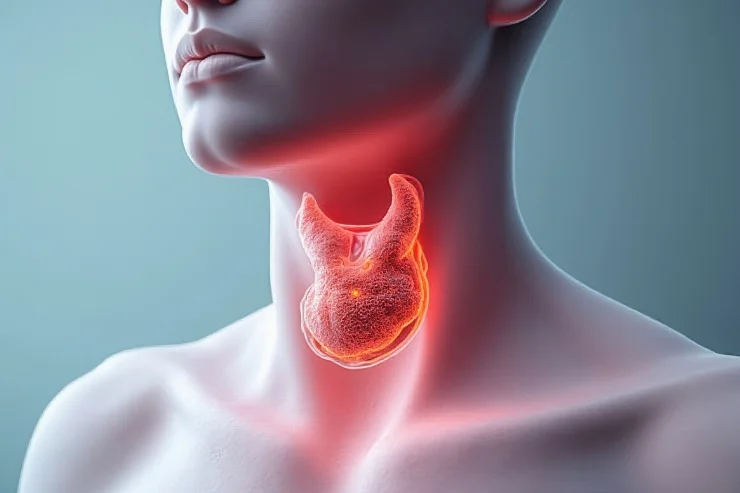
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer arises in the thyroid gland, a key regulator of metabolism. It often presents as a painless neck lump, voice changes, or difficulty swallowing. While some types are slow-growing, aggressive forms require prompt treatment. Risk factors include radiation exposure and family history. Diagnosis involves ultrasound and biopsy, while treatment options range from surgery and radioactive iodine therapy to targeted drugs. With early detection, most thyroid cancers have a high survival rate, emphasizing timely medical attention.
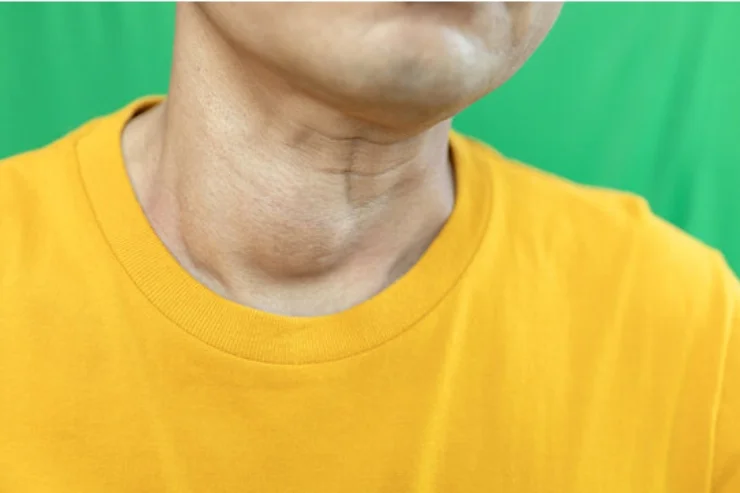
Laryngeal Cancer
Laryngeal cancer affects the voice box, leading to hoarseness, throat pain, difficulty swallowing, and breathing problems. It is strongly associated with smoking, alcohol, and HPV infection. Diagnosis involves imaging tests and biopsies, with treatment including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Early-stage cases may preserve voice function, while advanced cases require reconstructive procedures. Prevention focuses on lifestyle changes like quitting smoking. Advances in treatment have improved survival rates.
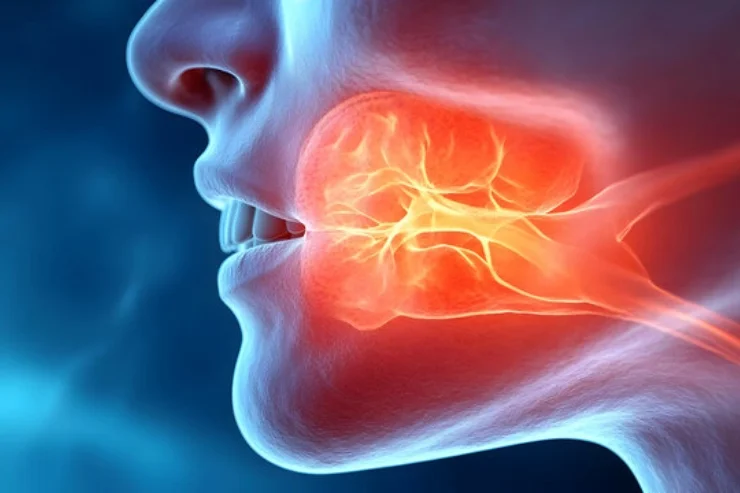
Parotid Cancers
Parotid cancers affect the largest salivary glands, leading to facial swelling, pain, and nerve dysfunction. Though rare, they can be aggressive, requiring surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. Causes remain unclear, but prior radiation exposure and genetic predisposition may increase risk. Diagnosis involves imaging and biopsy. Surgical removal is often necessary, sometimes involving facial nerve preservation. Early detection and specialized treatment improve prognosis. Regular checkups help monitor unusual growths, ensuring timely intervention for better patient outcomes.
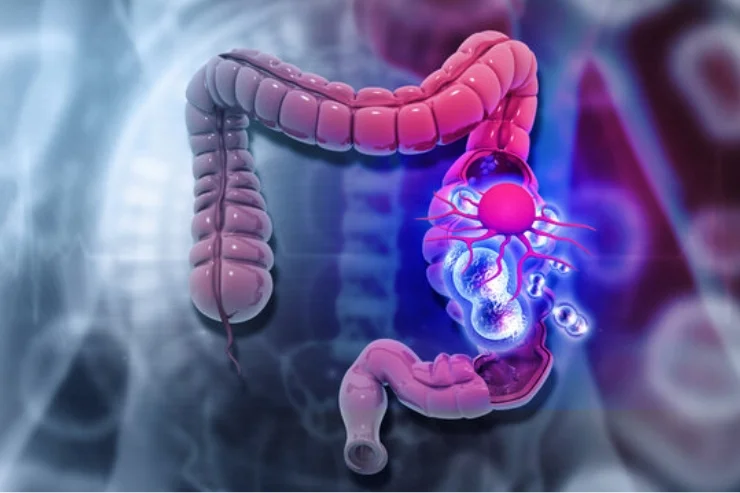
Colon and Bowel Cancers
Colon and bowel cancers develop in the large intestine, often starting as polyps that turn cancerous over time. Risk factors include poor diet, obesity, smoking, and family history. Symptoms include altered bowel habits, blood in stool, weight loss, and persistent fatigue. Screening via colonoscopy helps detect early changes. Treatment includes surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted therapies. Lifestyle modifications, fiber-rich diets, and regular screenings significantly reduce risk, emphasizing the importance of early detection for improved survival rates and better outcomes.

Gynaecological Cancers
Gynaecological cancers include cervical, ovarian, uterine, vaginal, and vulvar cancers. Symptoms vary but often include abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, bloating, or changes in discharge consistency. Risk factors range from HPV infection to hormonal imbalances and genetic mutations. Early detection through Pap smears, imaging, and genetic testing significantly improves treatment success. Treatment may involve surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or targeted therapies. Awareness, vaccinations, and routine checkups play a vital role in preventing, detecting, and managing these cancers effectively.
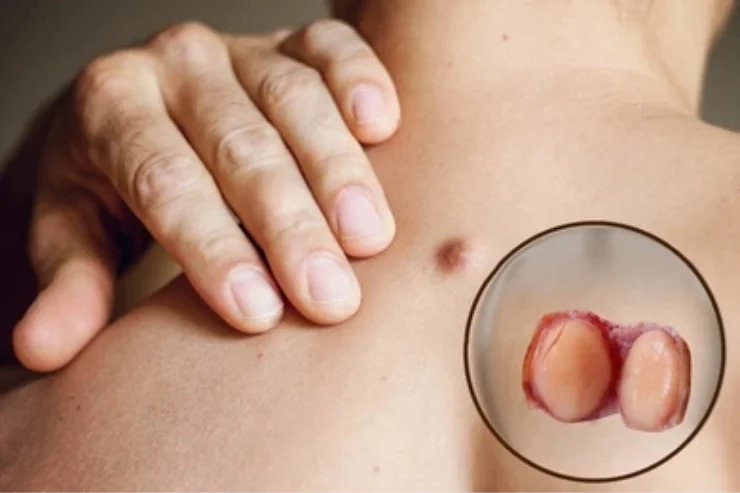
Soft Tissue Tumors
Soft tissue tumors arise in muscles, fat, nerves, or blood vessels, potentially becoming sarcomas. They may develop anywhere in the body, with symptoms including painless lumps that grow over time. Though causes are unclear, genetic factors and radiation exposure increase risk. Diagnosis involves imaging and biopsy, while treatment includes surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Early intervention improves outcomes, as aggressive sarcomas can spread. Regular monitoring of unusual growths aids in timely diagnosis and treatment.

Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers, affecting both men and women. Symptoms include lumps, nipple discharge, and skin dimpling. Risk factors include genetics, hormonal changes, and lifestyle factors. Diagnosis involves mammograms, biopsies, and imaging. Treatment options range from surgery and chemotherapy to targeted and hormone therapies. Regular screenings and self-examinations enhance early detection, improving survival rates. Lifestyle changes, including exercise and a healthy diet, can also help reduce risk.
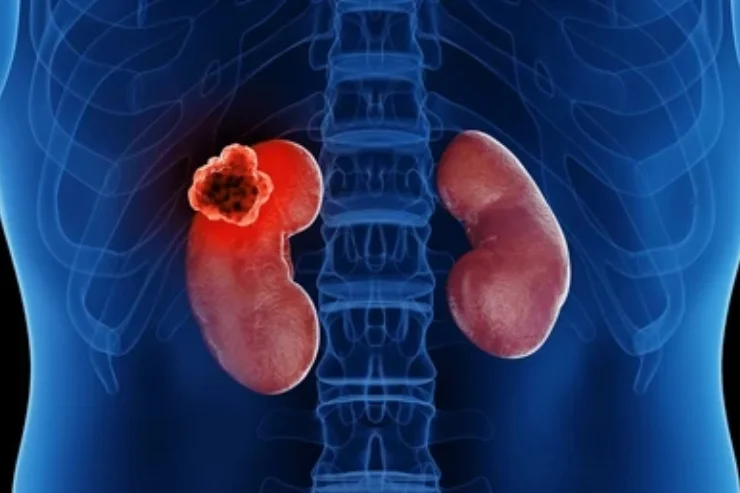
Renal Cancer
Renal cancer, or kidney cancer, originates in the kidneys and is often detected incidentally during imaging tests. Symptoms may include blood in urine, back pain, and unexplained weight loss. Risk factors include smoking, obesity, and high blood pressure. Diagnosis involves CT scans and biopsies, with treatments including surgery, immunotherapy, and targeted therapies. Early detection improves outcomes significantly, emphasizing the importance of regular checkups, timely intervention, and a healthy lifestyle to reduce risk.
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer arises from the bladder lining, commonly presenting with blood in urine, frequent urination, and pelvic pain. Smoking and chemical exposure increase risk. Diagnosis involves urine tests, cystoscopy, and imaging. Treatment varies based on stage, including surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. Early detection significantly improves survival rates, making awareness and routine screenings essential. Preventive measures include hydration, avoiding smoking, and limiting exposure to harmful chemicals linked to bladder cancer.
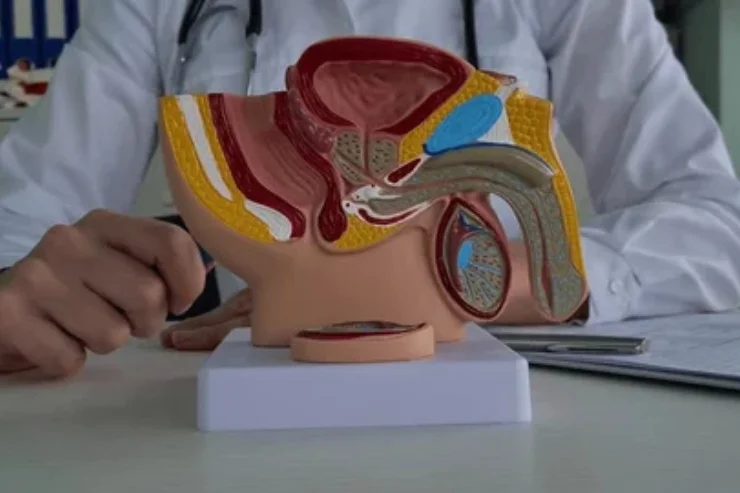
Penile Cancer
Penile cancer is a rare but serious condition, often linked to HPV infection and poor hygiene. Symptoms include sores, swelling, and foul-smelling discharge. Early diagnosis improves outcomes, with treatments ranging from surgery to chemotherapy and radiation. Preventive measures include HPV vaccination and proper hygiene practices. Though uncommon, awareness and early intervention are crucial in managing this cancer effectively and improving survival rates. Regular urological checkups help detect potential abnormalities early.
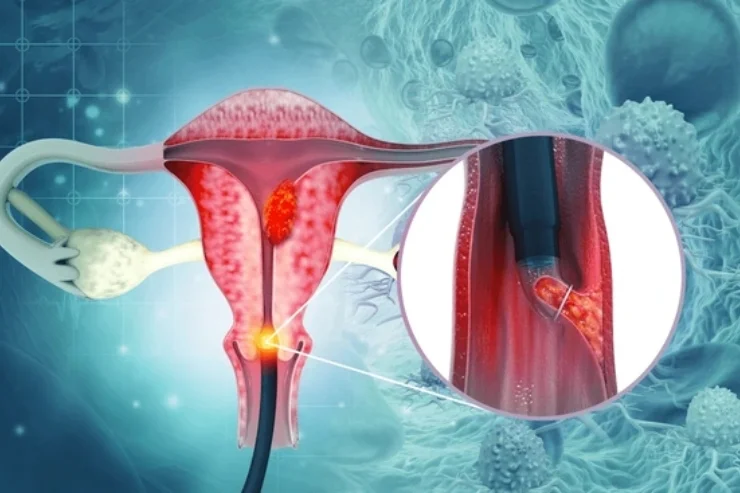
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer develops in the cervix, primarily caused by HPV infection. Symptoms include abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, and unusual discharge. Screening via Pap smears and HPV testing aids early detection. Vaccination against HPV significantly reduces risk. Treatment options include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Early detection ensures higher survival rates, emphasizing the importance of routine gynecological checkups. Awareness and preventive measures play a crucial role in reducing the global burden of cervical cancer.
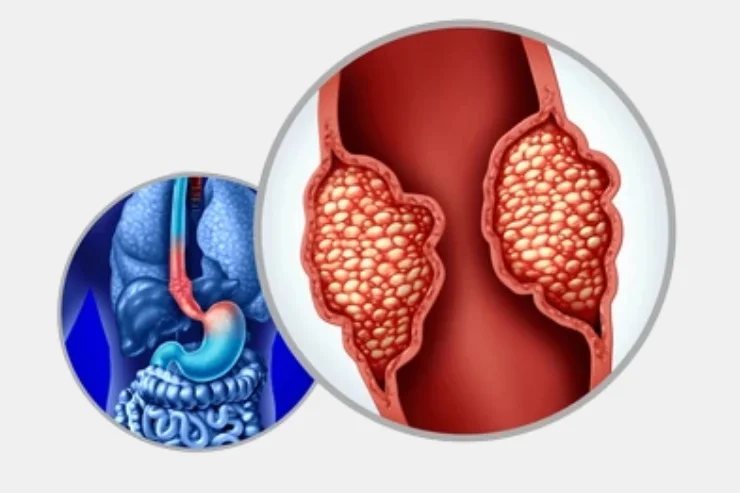
Stomach And Esophageal Cancers
Stomach and esophageal cancers affect the digestive tract, leading to difficulty swallowing, weight loss, nausea, and persistent acid reflux. Risk factors include smoking, alcohol, obesity, and Helicobacter pylori infection. Diagnosis involves endoscopy, biopsies, and imaging. Treatment includes surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies. Early detection improves survival rates, making routine checkups essential. Dietary modifications, avoiding tobacco, and managing acid reflux reduce risk, highlighting prevention as a key strategy in managing these cancers.